Page 8 - Dairy Dimension - Mar-Apr 2025
P. 8
| Volume 1 | Issue 3 | Mar-Apr 2025 ARTICLE | Volume 1 | Issue 3 | Mar-Apr 2025
Effect of Climate Change on safe, and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and 2. Impact on Forage and Feed Availability
regions.
preferences for an active and healthy life. Food security
Food Security of Dairy Animals is built upon four key pillars: India's dairy sector relies heavily on natural forages such
1. Availability – Sufficient food supply at local, national,
as grasses, legumes, and crop residues. Climate
and global levels.
and Their Performance 2. Access – Economic and physical means to obtain change—through erratic rainfall patterns, rising
temperatures, and frequent droughts—threatens the
food. supply and quality of these feed sources.
Dr Harsimran Kaur , Dr Simranjeet Kaur , Dr Harinder Singh , Dr Ramandeep Singh 4 3. Utilization – Proper use of food, including its · Decline in Forage Quality and Quantity
2
3
1
1& 2 Ph.D., Punjab Agricultural University; Excellent Enterprises, Khanna; nutritional quality and how the body absorbs In drought-prone states like Rajasthan, Maharashtra,
3
4 Professor, Punjab Agricultural University nutrients. and Gujarat, changing monsoon patterns have led to
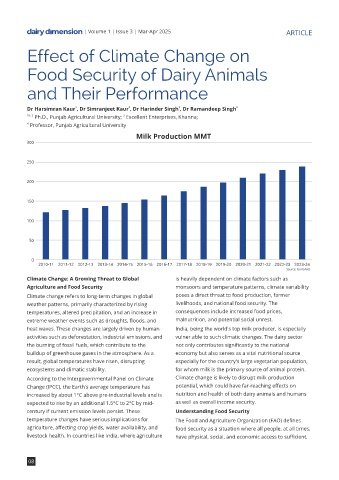
Milk Production MMT 4. Stability – Consistent availability and access to food declining fodder availability. Chakravarty et al. (2020)
300 over time, without disruptions. observed that repeated droughts are shrinking
Climate change threatens all these pillar—disrupting grazing lands, forcing farmers to rely on expensive
250 production through extreme weather, reducing access feed alternatives.
by harming agricultural incomes, compromising Moreover, elevated temperatures reduce forage
nutrition through lower-quality crops, and undermining quality by degrading nutrient content and increasing
200
system stability. indigestible fiber, thereby compromising dairy animal
1. Direct Effects of Climate Change on Dairy Animals health, productivity, and milk yield.
150 Rising Dependence on Commercial Feeds
· Heat Stress and Reduced Milk Production ·
One of the most immediate effects of climate change With natural forage becoming scarce, many farmers
100 on dairy animals is heat stress, particularly when are switching to commercial feeds, which are often
temperatures exceed 25–30°C. Cows and buffaloes costly and not easily accessible to smallholder
struggle to regulate their body temperature under farmers. Climate change also impacts global grain
50
such conditions, resulting in reduced feed intake, production, leading to price volatility and supply
lower milk yield, and impaired reproduction. In issues. Kumar et al. (2018) noted that fluctuating
0 regions like northern and central India, where grain prices linked to weather events in exporting
2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 2013-14 2014-15 2015-16 2016-17 2017-18 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22 2022-23 2023-24
Source: GoI DAHD summer temperatures can exceed 40°C, the effects countries have increased feed costs and further
Climate Change: A Growing Threat to Global is heavily dependent on climate factors such as are more severe. strained dairy farm profitability.
Agriculture and Food Security monsoons and temperature patterns, climate variability · Studies (Mader et al., 2006) indicate that milk 3. Economic Pressures on Smallholder Farmers
Climate change refers to long-term changes in global poses a direct threat to food production, farmer production may decline by 10–30% due to heat · India's dairy industry is largely made up of
weather patterns, primarily characterized by rising livelihoods, and national food security. The stress. Cows also show behavioural changes, such as smallholder farmers with limited livestock and
temperatures, altered precipitation, and an increase in consequences include increased food prices, increased resting time and reduced grazing, which minimal resources. These farmers are especially
extreme weather events such as droughts, floods, and malnutrition, and potential social unrest. leads to lower food intake (Singh et al., 2019). vulnerable to climate change
heat waves. These changes are largely driven by human India, being the world's top milk producer, is especially Elevated cortisol levels from stress negatively affect · Rising Costs and Reduced Incomes
activities such as deforestation, industrial emissions, and vulner able to such climatic changes. The dairy sector reproduction, causing delayed estrus and higher Increased expenses for feed, water, and veterinary
the burning of fossil fuels, which contribute to the not only contributes significantly to the national stillbirth rates care are cutting into already-thin profit margins.
buildup of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. As a economy but also serves as a vital nutritional source · Animal Health and Disease Risks Singh et al. (2019) estimated that climate-related
result, global temperatures have risen, disrupting especially for the country's large vegetarian population, Heat stress compromises the immune system, losses in productivity and rising costs could reduce
ecosystems and climatic stability. for whom milk is the primary source of animal protein. making animals more susceptible to diseases such as small farm incomes by 15–25%.
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Climate change is likely to disrupt milk production mastitis, respiratory infections, and foot rot. Ghosh Additionally, irrigation-dependent fodder crops are
Change (IPCC), the Earth's average temperature has potential, which could have far-reaching effects on and Samui (2020) found that stressed animals are at being affected by water scarcity, escalating local
increased by about 1°C above pre-industrial levels and is nutrition and health of both dairy animals and humans increased risk of infections, escalating veterinary tensions over water usage and threatening long-term
expected to rise by an additional 1.5°C to 2°C by mid- as well as overall income security. treatment costs. Additionally, rising temperatures sustainability.
century if current emission levels persist. These Understanding Food Security and altered rainfall also promote vector-borne · Threats to Food Security
temperature changes have serious implications for The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines diseases such as foot-and-mouth disease and Milk remains a vital source of nutrition for many
agriculture, affecting crop yields, water availability, and food security as a situation where all people, at all times, bluetongue. ICAR reports highlight the growing risk Indians, especially in rural areas. Disruptions in milk
livestock health. In countries like India, where agriculture have physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, by increased mosquito and tick activity in hotter
production can lead to supply shortages and price
08 09